This article is regarding how to implement dagger 2 with new approach, It brought giant change and in this way getting ride of boilerplate code through dagger 2.x new release. However I don’t compare between old and new dagger structure so I just have developed a simple sample from scratch about that and basically touch on @Component, @Module, @ContributesAndroidInjector, AndroidInjection.inject(this), AndroidSupportInjection.inject(this).
If you want to use these, first of all we should set up gradle:
Set up gradle:
kapt 'com.google.dagger:dagger-compiler:2.16'
kapt 'com.google.dagger:dagger-android-processor:2.16'
implementation 'com.google.dagger:dagger-android-support:2.16'i added kapt instead of annotationProcessor for kotlin. we dont need to keep annotationProcessor dependency. Also we have to add kotlin-plugin in gradle.
apply plugin: 'kotlin-kapt'
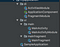
Basically Package Structure:
Let’s start to create ApplicationComponent interface that is root in our dagger graph. It may includes more modules that just listed here. For instance; api module, shared preference module and something like that. I started to add AndroidInjectionModule as a module in the component. This module should be installed in the component that is used to inject. AndroidInjectionModule also is internal module, it was created by Dagger, it includes binding activity, fragment, service, broadcastReciver and content provider. We will add ActivitiesModule module later on.
@Singleton
@Component(modules = AndroidInjectionModule::class)
interface ApplicationComponent {
fun inject(application: Application)
@Component.Builder
interface Builder {
fun build(): ApplicationComponent
@BindsInstance
fun applicationBind(application: Application): Builder
}
}Let’s start to write ActivitiesModule as a subcomponent, we will use @ContributesAndroidInjector annotation type. After that we will add it in ApplicationComponent as a module.
@Module
abstract class ActivitiesModule {
@ContributesAndroidInjector(modules = [(MainActivityModule::class)])
abstract fun contributeActivityAndroidInjector(): MainActivity
}@ContributesAndroidInjector can takes modules, Modules to be installed in the generated. I’ll explain the MainActiviyModule that what should include, also with @Bind annotation . By the way If module needs scope, we can create spesific Scope, for instance; @ActivityScope, @FragmentScope..
import javax.inject.Scope
@Scope
@MustBeDocumented
annotation class ActivityScopeif you need it, we can add scope like here.
@ActivityScope
@ContributesAndroidInjector(modules = [(ActivityModule::class)])
abstract fun contributeActivityAndroidInjector(): MainActivityDagger 2 includes HasActivityInjector as a new that provides AndroidInjector and should implement in Application class, also we should inject DispatchingAndroidInjector that’s mean return activityInjector, in this way we’ll use AndroidInjection.inject() for activity and fragment.
class SampleApplication : Application(), HasActivityInjector {
@Inject
lateinit var dispatchingAndroidInjector: DispatchingAndroidInjector<Activity>
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
DaggerApplicationComponent.builder()
.applicationBind(this)
.build()
.inject(this)
}
override fun activityInjector(): AndroidInjector<Activity> = dispatchingAndroidInjector
}We can use AndroidInjection.inject(this) in activity after inject DispatchingAndroidInjector in application.
AndroidInjection.inject(this) should calls in onCreate method before super. That’s all!!
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(){ override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
AndroidInjection.inject(this)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
}}
you can see generated file below that code was created by dagger after rebuild. Remember, via androidInjector.inject(this) we passed activity, it gets DispatchingAndroidInjector<Activity> from application.
private DispatchingAndroidInjector<Activity> getDispatchingAndroidInjectorOfActivity() {
return DispatchingAndroidInjector_Factory.newDispatchingAndroidInjector(
getMapOfClassOfAndProviderOfFactoryOf());
}DispatchingAndroidInjector looks up AndroidInjector.Factory, it is below the code snippet. it creates your activities subcomponent builder, and pass the activities to inject your activities.
private Map<Class<? extends Activity>, Provider<AndroidInjector.Factory<? extends Activity>>>
getMapOfClassOfAndProviderOfFactoryOf() {
return MapBuilder
.<Class<? extends Activity>, Provider<AndroidInjector.Factory<? extends Activity>>>
newMapBuilder(2)
.put(MainActivity.class, (Provider) mainActivitySubcomponentBuilderProvider)
.put(SecondActivity.class, (Provider) secondActivitySubcomponentBuilderProvider)
.build();
}Inject Fragment Object
So far, We injected Activity object.Well, How we can inject fragment object. We will modify activity class to inject fragment object and implement HasSupportFragmentInjector or HasFragmentInjector interface. HasSupportFragmentInjector is for android.support.v4.app.Fragment and HasFragmentInjector is for android.app.Fragment after that we pass fragment in DispatchingAndroidInjector, that’s looks here.
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), HasSupportFragmentInjector {
@Inject
lateinit var dispatchingAndroidInjector: DispatchingAndroidInjector<Fragment>
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
AndroidInjection.inject(this)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
}
override fun supportFragmentInjector() = dispatchingAndroidInjector
}Also, we create Fragment module same way with the activity.
@Module
abstract class FragmentModule {
@ContributesAndroidInjector
abstract fun contributeMainFragment(): MainFragment
}If you need to add MainFragmentModule, simply add like this;
@ContributesAndroidInjector(modules = [(MainFragmentModule::class)])
we should specify FragmentModule in our root graph after created fragment module
@Component(modules = [AndroidSupportInjectionModule::class,
ActivitiesModule::class,
FragmentModule::class])now we can inject fragment object. For fragment we can call AndroidSupportInjection.inject(this) in onAttach method before super.
class MainFragment : Fragment() {
override fun onAttach(context: Context?) {
AndroidSupportInjection.inject(this)
super.onAttach(context)
}
override
fun onCreateView(inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?): View? {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.main_fragment, container, false)
}
}That’s all:) You also can find source code GitHub.